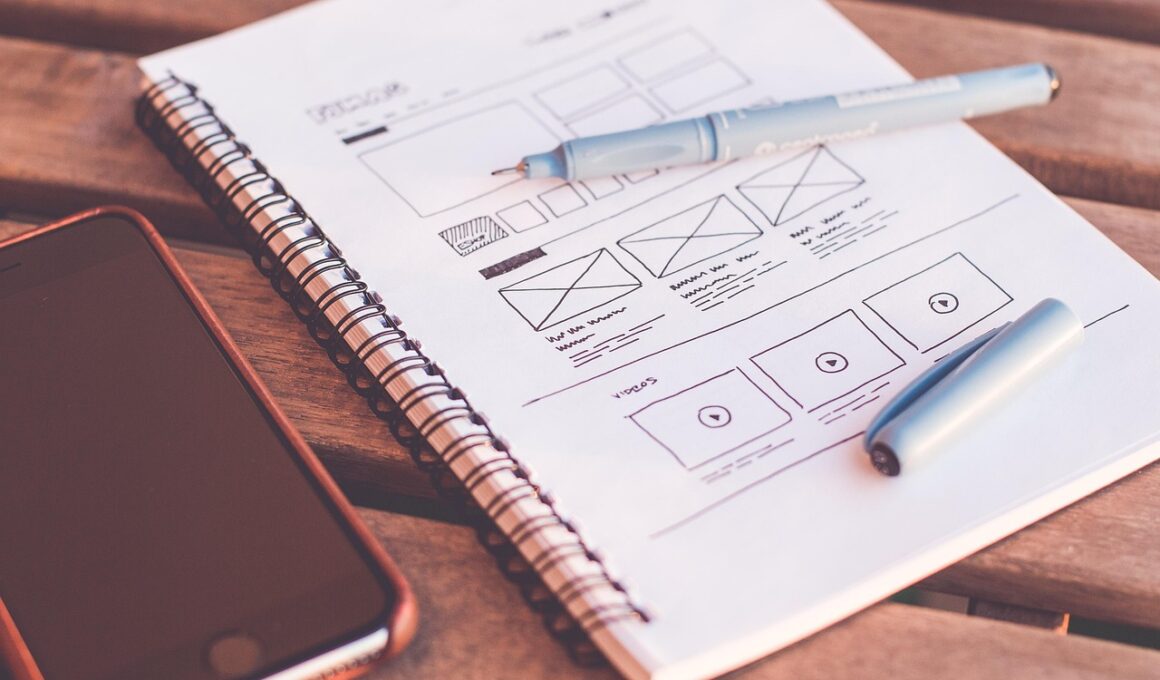
Rapid Prototyping and Testing in Design Thinking
Rapid prototyping is crucial within the design thinking method. This approach encourages innovation by allowing designers to visualize concepts quickly and receive immediate feedback. With rapid prototyping, teams can experiment with various designs visually without dedicating excessive resources or time upfront. This iterative process enables designers to create physical or digital representations of ideas that can be tested, examined, and refined. Quick feedback from users or stakeholders ensures that potential issues are identified early, fostering a more collaborative environment. Moreover, this method reduces the risk of developing a final product that does not align with user expectations or needs. There are multiple forms of rapid prototypes, including sketches, wireframes, mockups, and functional models. Each form aids in uncovering vital insights about user interactions. This practice also embodies a core principle of design thinking: putting the user at the center of the design process. The quicker feedback cycles not only enhance the end product but also engage users in a more meaningful way. Thus, rapid prototyping becomes an invaluable tool for creative teams. Utilizing these techniques can transform the innovation landscape significantly.
In the context of design thinking, testing is as important as prototyping. Testing refers to the evaluation of the prototype to understand its effectiveness in solving specific problems the users face. It involves collecting qualitative and quantitative data that can help guide design refinements. In this phase, teams deploy various testing methods, including usability tests, interviews, and surveys. By incorporating the voice of the user, designers gain invaluable insights on interactions and overall satisfaction. This process encourages iterative modifications, where feedback is directly implemented into subsequent prototypes. This not only enhances the product but also aligns it more closely with user expectations. Testing ensures that the solutions devised are both viable and desirable for the intended audience. Rapid iterations enable teams to navigate through assumptions and validate hypotheses about their designs. By fostering an open mindset towards failure, testing helps to identify what works and what doesn’t. This information is instrumental in making informed design decisions moving forward. Ultimately, the testing phase of design thinking fosters a level of resilience and adaptability, critical for successful innovation.
The Role of User Feedback
User feedback is fundamental to the rapid prototyping and testing phases of design thinking. It allows designers to gauge how well their prototypes resonate with real users. Early and frequent feedback loops, created through user interactions with prototypes, are indispensable in refining concepts. This two-way communication helps teams adjust functionalities, features, or even aesthetics based on genuine user experiences, eliminating guesswork. By actively engaging with users, designers can discover nuanced insights about their needs, frustrations, and desires that might not have emerged during initial research phases. Collecting user feedback can take many forms, such as direct observations during usability tests, feedback sessions, and iterative surveys. Each interaction offers designers an opportunity to gather rich contextual data about how users interact with their products. Additionally, user feedback directly influences the emotional reaction users have toward solutions. Therefore, cultivating strong relationships with users at early stages is essential. This connection helps foster an environment of trust and collaboration, making users more willing to provide constructive feedback, which is invaluable for the design refinement process.
Another critical aspect of rapid prototyping and testing in design thinking involves the concept of iteration. Iteration suggests that designs should evolve through repeated cycles. As teams gather data from testing feedback, they refine and retest their prototypes, creating a seamless loop of improvement. This iterative process encourages creativity and exploration, empowering designers to push boundaries. Moreover, embracing an iterative mindset offers an opportunity to integrate new ideas and perspectives into designs, avoiding stagnation. Each iteration brings the potential for significant breakthroughs. Furthermore, by breaking a project into smaller, manageable components, teams can focus on specific functionalities or features during each cycle. This focus enables concentrated thought on different aspects of the user experience, facilitating comprehensive redesigns. Additionally, teams become more adept at identifying successful strategies and approaches with each iteration. Adopting this methodology instills a culture of experimentation, prompting teams to embrace failure as a valuable learning opportunity. Thus, iteration in rapid prototyping and testing is not just a strategy but a philosophy underpinning innovative design thinking practices.
Technology in Rapid Prototyping
Advancements in technology have significantly transformed rapid prototyping methods, making them more efficient and accessible. Various software tools and applications exist that allow designers to create high-fidelity prototypes quickly. Technologies like 3D printing enable teams to develop tangible products at a faster pace than traditional methods. Moreover, digital prototyping tools, such as Sketch, Figma, or Adobe XD, allow for the creation of interactive wireframes that can simulate user experiences effectively. These tools facilitate collaboration among team members, ensuring they can contribute to prototype development seamlessly, regardless of their geographical locations. Additionally, virtual reality and augmented reality platforms provide immersive experiences, allowing users to interact with designs more deeply. This level of engagement yields richer feedback and validates concepts in ways that traditional methods cannot offer. The integration of these technologies into design thinking encourages innovation, pushing designers to explore uncharted territories. As a result, rapid prototyping not only speeds up the design process but also enhances creativity and exploration within projects, empowering teams to take calculated risks while embracing new methods.
As teams embark on their rapid prototyping and testing journeys, establishing clear objectives for each prototype is essential. Defining the purpose of a prototype ensures that teams remain focused on solving specific user problems. This clarity helps guide design decisions, preventing scope creep or diluted objectives. Each prototype serves a unique purpose, whether it’s exploring a new feature, evaluating usability, or validating a concept. By aligning design objectives with direct links to user feedback, designers can prioritize the most impactful changes effectively. Furthermore, setting measurable goals for user interactions, such as time spent on tasks or error rates, is equally vital. These metrics provide concrete evidence of success during testing phases. Additionally, the design teams should engage in post-session analyses, reflecting on the results to identify areas for improvement. This introspective review fosters a deeper understanding of user behaviors and reactions, feeding back into the design process. Thus, established objectives in rapid prototyping and testing ensure that the design thinking approach remains user-centered, strategic, and results-driven, facilitating meaningful outcomes.
Conclusion: The Future of Design Thinking
The integration of rapid prototyping and testing into design thinking practices represents a paradigm shift in innovation approaches. By emphasizing user involvement, iteration, and technology, the design thinking process continually adapts to meet changing needs. This focus on collaboration ensures that design solutions remain relevant and impactful. Furthermore, as technology evolves, designers will be able to leverage even more sophisticated tools to enhance their rapid prototyping efforts. Future innovations in AI and machine learning could predict user behaviors, suggesting design modifications before feedback is necessary. This potential revolution in design thinking highlights the importance of embracing change. It reframes the traditional product development process, resulting in more empathetic and effective user experiences. Ultimately, effective implementation of rapid prototyping and testing requires a commitment to learning and adaptation across project teams. By fostering a culture of innovation, organizations can unlock new levels of creativity and ideas. As such, the potential of design thinking in elevating user experience is boundless, positioning organizations to thrive in an increasingly complex and dynamic world.