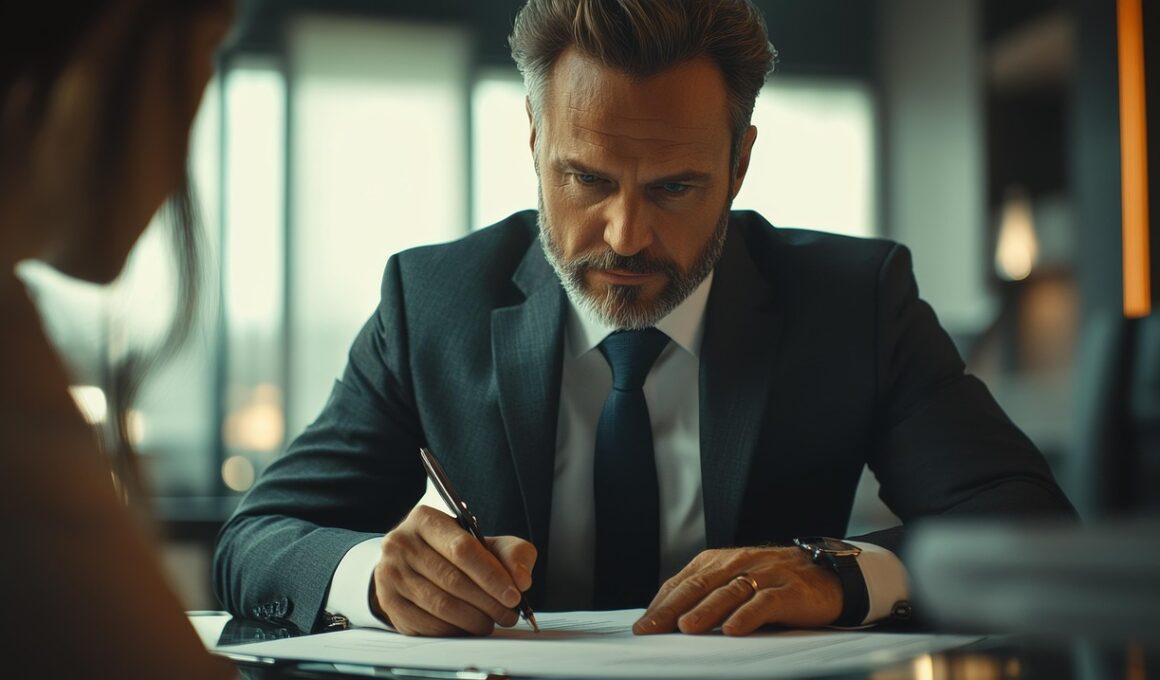
The Impact of Executive Compensation on Company Governance
Executive compensation is a crucial element of corporate governance that significantly influences managerial behavior and firm performance. As companies seek to align their leaders’ goals with shareholder interests, the structure of these compensation packages can shape strategic decision-making and risk-taking. High-performance incentive plans often drive executives to undertake riskier projects in pursuit of greater financial rewards. This dynamic introduces both opportunities for growth and challenges for governance structures, which must carefully balance risk with sustainable development. Furthermore, compensation committees are tasked with designing packages that incentivize long-term value creation rather than short-term earnings. As a result, the influence of executive pay on governance remains a focal point of corporate strategy discussions. Stakeholders, particularly shareholders, demand transparency and accountability in how compensation packages are structured and maintained. Analyzing governance case studies provides valuable insight into how effectively companies manage executive pay to create value. This exploration sheds light on best practices and potential pitfalls related to executive compensation, particularly in sectors with rapid change and volatility. Thus, understanding this relationship is essential for both current practitioners and future leaders in adapting governance frameworks effectively.
CEO Pay and Company Culture
The intersection of CEO pay and company culture illustrates the broader implications of compensation strategies on corporate governance. High executive compensation can foster a culture of entitlement, potentially alienating employees if not implemented with transparency and fairness. Executives may feel pressure to achieve targets that could compromise ethical standards, leading to detrimental behaviors for the overall organizational culture. Conversely, when compensation is linked to measurable performance metrics, it can promote a culture of accountability and results-focused actions. Research suggests that firms with well-aligned compensation structures often cultivate a workforce committed to shared goals. The role of the board of directors is crucial in ensuring these payments reflect the company’s long-term strategy rather than individual executive interests. Additionally, incorporating stakeholder feedback into compensation decisions can enhance trust and collective commitment. Regular audits of compensation practices help identify discrepancies and address potential conflicts related to governance. Therefore, understanding the cultural implications of executive pay is vital for fostering a positive work environment while ensuring effective company governance. By emphasizing ethical considerations alongside financial incentives, companies guarantee a more resilient organizational culture.
Another important aspect of executive compensation is its impact on corporate risk management practices. High levels of executive compensation, particularly through stock options, may incentivize risk-taking behavior that undermines financial stability. A compensation structure poorly aligned with the company’s long-term strategy can lead executives to prioritize immediate gains at the expense of sustainable growth. In situations where market conditions fluctuate, this misalignment can provoke disastrous consequences for the organization, affecting stakeholders significantly. Effective governance frameworks must therefore ensure that compensation packages incorporate elements that discourage excessive risk-taking. Salary structures should ideally include clawback provisions or multi-year performance vesting to mitigate excessive risk-seeking behavior. Furthermore, boards must remain vigilant in monitoring market changes as a means to adjust executive compensation strategies accordingly. Transparent communication regarding risk factors and performance metrics will foster a culture of responsible risk management in the organization. By revisiting these practices, firms can better safeguard their long-term viability while ensuring stakeholder interests are prioritized at all levels. Ultimately, by aligning executive incentives with sustainable goals, companies manage to reinforce their governance structures.
Shareholder Activism and Compensation Practices
Shareholder activism has emerged as a critical force in shaping executive compensation practices, compelling boards to reevaluate their strategies. Activist shareholders wield significant influence by advocating for changes that align executive pay with long-term performance. They challenge excessive remuneration packages that do not yield commensurate returns, pressing for enhanced transparency in compensation structures. Consequently, boards of directors are increasingly held accountable for executive pay decisions and are more responsive to shareholder concerns. Activists may advocate for adjustments or caps to executive compensation to mitigate perceived inequalities within the organization. This push for responsible governance attracts additional attention from investors seeking ethical firms. Also, activism often results in shareholder proposals to restructure management incentives, fostering a conversation around equitable compensation practices. The emerging emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors adds another layer of complexity to compensation discussions, as organizational leaders must balance financial performance with societal impacts. As this trend progresses, companies must develop governance frameworks that integrate shareholder feedback while retaining crucial elements of executive incentive structures. Engaging with shareholders will further enhance mutual understanding and support for strategic objectives.
Another critical element in analyzing executive compensation is the impact of market comparisons on governance structures. Organizations often benchmark their executive pay against industry peers to ensure competitiveness and attract top talent. While this practice aims to optimize the attractiveness of executive roles, it can inadvertently contribute to the escalation of compensation across the sector. As companies compete for leadership talent, they may offer outsized salaries, leading to a compensation arms race that doesn’t strictly correlate with performance. This escalating trend can debase governance practices, diverting funds away from investments that foster company growth. Shareholders, thus, must play a proactive role in monitoring compensation trends while advocating for accountability among executive leaders. Effective governance should apply consistent scrutiny of compensation decisions against performance, emphasizing the need for performance-based evaluations and incentives. Evaluation methodologies should evolve to incorporate qualitative and quantitative metrics, ensuring comprehensive assessments. This approach contributes to a culture of continuous improvement in governance standards, counteracting any detrimental trends resulting from aggressive market comparisons. By prioritizing value creation over mere competitiveness, organizations reinforce their governance foundation.
Ethics in Compensation Governance
The ethical implications surrounding executive compensation are increasingly becoming prominent in discussions of corporate governance. As the divide between executive pay and average employee wages continues to widen, concerns emerge regarding fairness and equity within companies. Stakeholders now prioritize ethical frameworks that encourage responsible governance practices, compelling organizations to reconsider their compensation strategies. Engaging in fair practices contributes to employee morale and brand reputation, bolstering overall organizational integrity. Companies that adopt an ethical approach to executive pay often demonstrate increased transparency and justify compensation structures through comprehensive rationale. Incorporating stakeholder perspectives into compensation decisions fosters trust and collective commitment, allowing organizations to thrive in competitive landscapes. Boards must prioritize ethical considerations alongside financial incentivization to establish a positive company culture. Moreover, defending compensation decisions requires a robust dialogue reflective of the organization’s values, providing clarity around executive roles and their relative compensation. Establishing this ethical grounding not only enhances corporate governance but also strengthens stakeholder relationships, promoting shared values and mutual respect among all organizational levels. Furthermore, this approach will help in attracting and retaining top talent who resonate with these values.
Lastly, the influence of regulatory frameworks on executive compensation cannot be overlooked in discussions about corporate governance. As regulations evolve, companies must adapt their compensation practices to remain compliant while maintaining competitive edge. Legislative changes often aim to enhance transparency around executive pay and incentivize alignment with shareholder interests. Initiatives such as say-on-pay votes provide shareholders with opportunities to voice opinions regarding compensation packages that require careful consideration by boards. These voting mechanisms compel organizations to justify their compensation structures and foster accountability. Additionally, regulatory frameworks encourage firms to disclose compensation details, enhancing overall transparency in governance practices. Therefore, corporate leaders must stay informed about regulatory changes and consider their long-term implications on executive compensation decisions. Compliance with standards must not only be seen as a legal requirement but also as a means of building credibility and trust with all stakeholders. By embracing these regulations positively, firms can create robust governance frameworks that emphasize both accountability and ethical responsibility while enhancing their competitiveness in the market.
To conclude, the dynamic relationship between executive compensation and corporate governance shapes the overarching business landscape. Organizations have a unique opportunity to leverage compensation practices to promote ethical behavior, align with stakeholder interests, and foster inclusive company cultures. By engaging executives through performance-based incentives that emphasize long-term success, firms can cultivate robust governance structures. Additionally, staying attuned to shareholder feedback and regulatory pressures will ensure compensation practices evolve effectively over time. The shift towards considering ethics in compensation highlights the increasing importance of social responsibility in executive pay discussions. Ultimately, the analysis of governance case studies reveals best practices around executive compensation and mitigation strategies for managing risks associated with excessive pay structures. As companies navigate these challenges, prioritizing ethical considerations in governance will create a sustainable environment for long-term growth. Corporate leaders that embed these principles within their organization’s culture will not only achieve superior performance outcomes but also fortify shareholder trust. In this era of rapid change and hyper-competition, understanding the nuances of executive compensation is essential for informed decision-making in corporate governance.