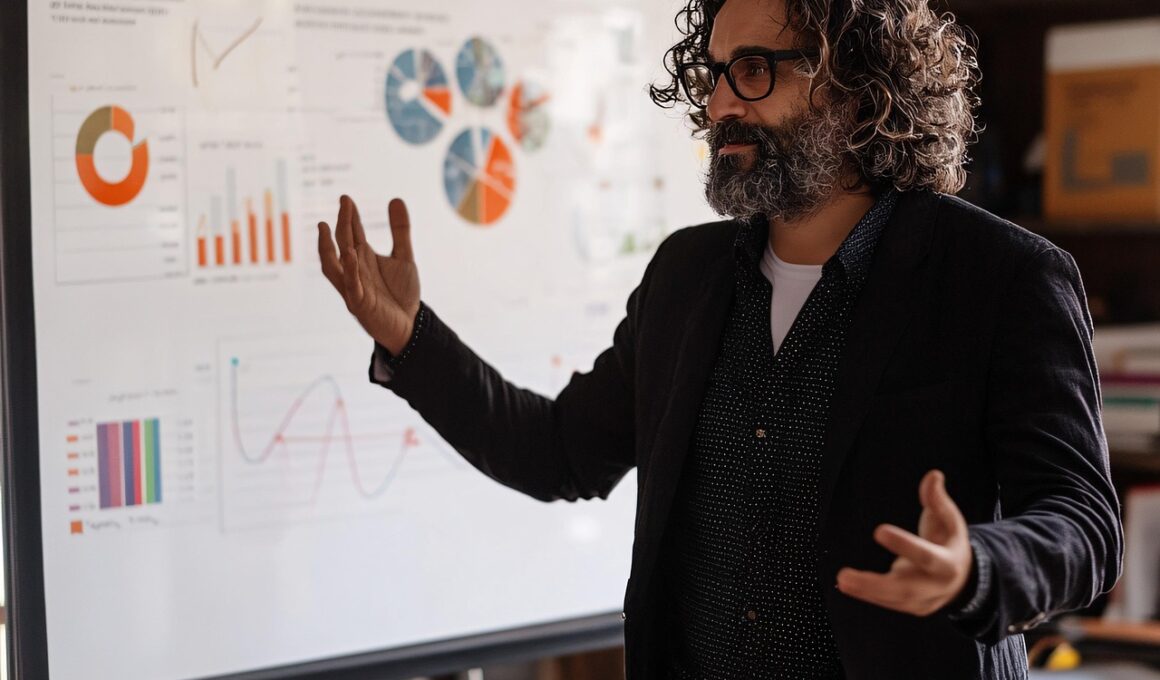
Designing Data Visualizations for Non-Technical Audiences
In today’s data-driven world, effective data visualization is crucial for communicating insights. Many professionals, particularly those without a technical background, struggle to interpret complex data sets. To bridge this gap, creating clear and engaging visual representations is essential. The goal is to convey meaningful information visually to promote understanding and decision-making. For instance, instead of presenting raw data, one might use bar charts, pie charts, or other graphics that highlight trends or comparisons. This approach helps audience members who may not have deep statistical knowledge. Color, shape, and layout significantly influence perception, so designers must be thoughtful in their selections. Using stark contrasts can emphasize important metrics, while muted colors can support secondary data points. Moreover, it’s vital to keep visualizations simple, avoiding unnecessary clutter. Too much information can overwhelm a viewer, leading to misinterpretation. Clear titles and concise annotations can guide the audience through the data. Balancing aesthetic appeal while ensuring clarity is the key goal in creating these visualizations. Ultimately, effective designs can drive better business decisions and foster a data-informed culture across organizations.
Elements of Effective Data Visualizations
When developing data visualizations, several fundamental elements contribute to their effectiveness. First, one must prioritize clarity over complexity. Trying to convey too much information at once can confuse the audience. Therefore, designers should focus on key messages that emerge from the data. Second, the use of appropriate chart types is essential. Different charts serve varying purposes; for instance, line graphs are great for trends over time, while bar graphs can effectively compare quantities. Third, color plays a vital role in visualization. Utilizing a consistent color scheme not only enhances aesthetics but also aids in comprehension. It’s crucial to ensure that colors are distinguishable for individuals with color vision deficiencies. Additionally, labels and legends are indispensable. Proper labeling gives context to the visual elements, ensuring the viewers understand what they’re observing. Furthermore, considering the target audience’s familiarity with data representations can guide design choices. For example, simpler visuals may suit a business audience, while more intricate designs might engage technical teams better. Overall, understanding these elements leads to the creation of visuals that resonate with non-technical audiences.
Moreover, interactive elements have gained popularity in data visualizations, especially for engaging non-technical audiences. By allowing users to explore data at their own pace, interactivity can enhance understanding and retention. Features like hover-overs, clickable filters, and zoom functionalities enable users to delve deeper into specific areas of interest. These technologies cater to diverse audience learning styles, making data exploration a more personalized experience. When designing interactive visualizations, it’s important to maintain a seamless user experience. That ensures non-technical users don’t feel overwhelmed. Therefore, tutorials or guided walkthroughs can be helpful. They provide users with a clearer understanding of how to utilize interactive features effectively. Another consideration is the use of storytelling techniques within presentations. Framing data within a narrative context can significantly aid comprehension. Instead of mere facts, weaving insights into a story engages emotions and fosters a stronger connection to the information. Anchoring visualizations to real-life scenarios enhances relatability. Thus, using relatable examples in conjunction with data helps the audience grasp the significance of insights. Ultimately, a blend of interaction and narrative fosters a rich data exploration experience for all users.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Creating data visualizations can be rewarding, but several pitfalls may impede effectiveness. One common mistake is overcomplicating visuals with excessive details. Data visualizations should communicate key insights quickly and clearly. Complex designs laden with too many graphics can lead to viewer confusion. Hence, clarity should always take precedence over style. Another frequent issue arises from inadequate context. Providing background information helps audiences understand the data’s relevance and implications. Without context, even well-designed visuals can leave viewers puzzled. Misleading scales or proportions in charts can distort truths and lead to incorrect interpretations. To prevent confusion, ensure that scaling is uniform and accurately represented to viewers. Additionally, underestimating the impact of audience needs is crucial. Understanding the expectations, challenges, and preferences of the intended audience can significantly improve visual effectiveness. Researching the audience background could reveal insights about their familiarity with the data type. Providing pertinent details helps focus on significant trends. Finally, neglecting to review for errors and typos before dissemination can damage credibility. Always double-check data sources and presentational aspects for a polished and professional final product.
Lastly, the importance of testing visualizations before sharing them cannot be overstated. Engaging true representative users to assess the effectiveness of your designs yields invaluable insights. Feedback concerning clarity, usability, and effectiveness can help uncover blind spots that developers may overlook. Such reviews can lead you to refine visuals to ensure they resonate more effectively with audiences. Iteration based on user feedback is a standard best practice in design. Therefore, embedding this process fosters both ongoing improvement and confidence among stakeholders in the visuals produced. Using analytical tools that track how users interact with visualizations provides helpful data to enhance future projects. Monitoring patterns in user engagement and understanding where users lose interest allows further refinement. Furthermore, fostering an ongoing dialogue with users deepens the engagement, leading to richer data-driven discussions. It encourages a culture of continuous learning and adaptation among data professionals. By prioritizing user testing, data visualization creators can ensure their work resonates meaningfully with non-technical audiences. Ultimately, this will foster a deeper understanding of data across various industries.
Conclusion on Effective Data Visualization
In conclusion, designing data visualizations for non-technical audiences involves understanding their unique needs and preferences. Success lies in creating visuals that are not only informative but also engaging and accessible to all viewers. By focusing on clarity, choosing appropriate formats, and considering interactivity, practitioners can produce materials that effectively communicate vital insights. Awkward data representations can alienate audiences; hence a thoughtful approach that embraces simplicity without sacrificing substance is essential. Avoiding common pitfalls enhances visual effectiveness and encourages a greater appreciation for data’s role in decision-making. Ultimately, fostering a dialogue around visualizations promotes better understanding and facilitates a data-driven culture within organizations. Testing visuals ahead of distribution can yield valuable insights for continual improvements. Keeping up with the latest trends and technologies in the field can further sharpen visualization skills. As data becomes an increasingly critical asset, effective visualization will remain fundamental to communicating insights. Thus, staying attuned to users’ requirements will help data professionals craft visuals that lead to informed decision-making. In sum, these techniques will undoubtedly bridge the gap between complex data and non-technical audiences.
In the world of business analytics, harnessing the power of data in a meaningful way is vital. Creating data visualizations tailored for non-technical audiences ensures insights are accessible and impactful. The techniques discussed will help bridge communication gaps, enhancing understanding among varied stakeholders. Encouraging widespread data literacy will empower teams across an organization to leverage data-driven insights effectively. This focus on approachability in design will support business strategies that capitalize on data analysis. Therefore, organizations should prioritize developing the skills necessary to create effective visualizations that resonate with every audience member. By fostering an understanding of how to effectively convey their narratives, professionals can contribute to a culture of data-driven decision-making. Ultimately, well-designed data visualizations can create a competitive advantage, informing and accelerating business processes by making insights approachable and actionable. The ongoing evolution of tools will continue to enable better visualization practices, paving the way toward clearer communication in the burgeoning data landscape. As data analytics becomes more integral to organizational success, equipping teams with visualization skills will usher in a new era of understanding and utilization.
Resources for Further Learning
For those eager to deepen their understanding of creating effective data visualizations, numerous resources are available. Online courses are an excellent way to gain structured knowledge and practical experience. Websites like Coursera and Udemy offer classes ranging from beginner to advanced levels focused on data visualization tools and techniques. Additionally, books on design principles address how to effectively communicate data visually. Titles such as “The Visual Display of Quantitative Information” by Edward Tufte provide foundational insights into effective visualization practices. Participating in webinars and workshops can also provide fresh perspectives on current trends and technologies. Many experts share their experiences and strategies in these formats, enhancing the learning experience. Networking with professionals in the field through platforms like LinkedIn can lead to valuable collaborations and knowledge exchange. Finally, regularly reviewing case studies of successful data visualizations can inspire and inform future projects. By exploring diverse resources, individuals can significantly enhance their visualization skills.