Optimizing Supply Chain Management with Edge Computing
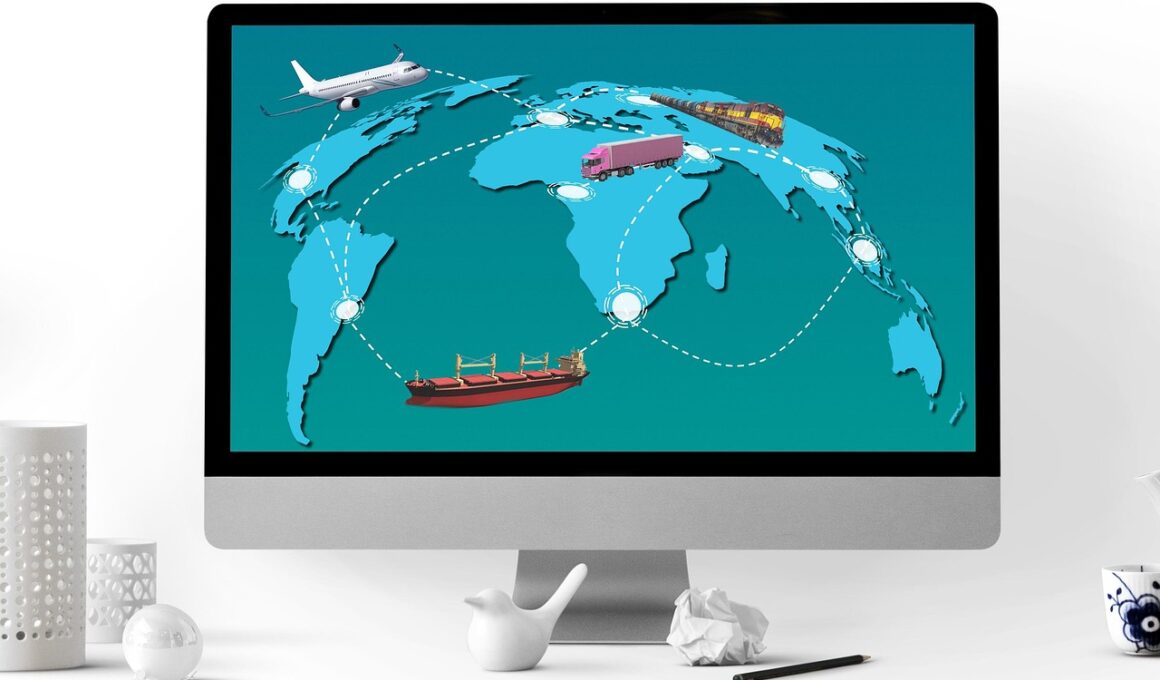
As businesses strive for excellence in supply chain management, edge computing presents transformative opportunities. By processing data closer to the sources, companies can enhance operational efficiency. This technology reduces latency, allowing for real-time analytics. A key benefit is improved visibility across the entire supply chain. Businesses have access to important data on inventory levels, shipment statuses, and supplier performance instantaneously. This leads to better decision-making and agility in responding to disruptions. Moreover, edge computing minimizes bandwidth costs by transmitting only relevant information to central cloud systems. Companies can utilize automated solutions for data collection and processing at production sites. By integrating edge computing with existing enterprise resource planning systems, companies can ensure smooth coordination between supply chain activities. This seamless integration enhances data accuracy and reliability. As a result, businesses can reduce operational delays and improve customer satisfaction by ensuring timely deliveries. In addition, companies adopting edge computing are positioned to utilize predictive analytics effectively, allowing them to forecast demand accurately and plan accordingly. The advantages of edge computing are becoming crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their supply chains and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced market.
With the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in edge computing, supply chain management reaches new heights. IoT devices provide critical data that enhances operational insights significantly. For example, sensors attached to vehicles can monitor conditions in real-time, helping to ensure that goods are transported efficiently. This immediate awareness of potential issues allows businesses to take proactive measures rather than reactive ones. Additionally, wearable technology for warehouse employees can increase productivity and safety by providing hands-free communication and tracking systems. Real-time data feedback helps supervisors manage workflows effectively and optimize routes for deliveries and pickups. Companies leveraging this combination can achieve unparalleled levels of efficiency. Furthermore, edge computing augments the ability to analyze large volumes of data generated by these IoT devices. Advanced analytics capabilities empower businesses to identify trends and improve operational strategies actively. Companies can also leverage this data to enhance customer interactions and experience through personalized engagement. By accurately predicting supply chain disruptions or spikes in demand, organizations can adapt more efficiently. Therefore, harnessing edge computing alongside IoT solutions is essential for any company looking to thrive in modern supply chain dynamics.
Enhancing Data Security
Data security is critical, especially in supply chains rich with sensitive information. Edge computing offers enhanced security measures by processing data locally. This reduced data movement decreases the chances of cyber-attacks during transmission. By retaining data within localized networks, businesses can better control who accesses that information. Additionally, edge devices equipped with robust security protocols can protect critical operational data from vulnerabilities. Implementing encryption and authentication processes at the edge ensures data integrity, making it harder for unauthorized access. Furthermore, companies can utilize machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and threats in real-time. This proactive approach enables businesses to respond to potential breaches immediately. With regulations around data protection tightening, complying with standards such as GDPR or CCPA is imperative. Edge computing allows organizations to meet these requirements while maintaining operational efficiency. Companies can segment sensitive data, ensuring that only necessary information is shared while minimizing exposure. Enhancing security measures at the edge leads to improved trust between partners and customers, crucial for effective collaboration. Thus, tightly integrating security within supply chain processes is not just a requirement but a business imperative that edge computing supports effectively.
Reducing operational costs through the utilization of edge computing plays a crucial role in supply chain optimization. By lowering latency and improving the speed at which data is processed, businesses find significant efficiencies. Real-time analytics empower organizations to minimize inventory levels while still meeting demand. Consequently, companies avoid the high costs of overstocking or stockouts. Furthermore, the localized processing of data reduces reliance on centralized cloud solutions, which can accumulate costs over time. As operational expenses decrease, profits are redirected towards innovation, enhancing competitiveness. Companies can also automate numerous supply chain tasks previously performed manually, further reducing labor costs. Automated systems minimize human error, optimizing accuracy in order fulfillment and inventory handling. By integrating edge applications with existing systems, businesses streamline operations and shorten decision-making cycles. Fostering a lean supply chain through improved efficiency and reduced waste leads to long-term sustainability. Knowing when to implement changes according to demand forecasts is vital for success. Streamlining logistics helps minimize downtime and operational disruptions, enabling smoother transitions between processes. Following this path ensures the enduring success and adaptability of businesses amid evolving market conditions and customer preferences.
The Role of Predictive Analytics
Another critical component of successfully employing edge computing in supply chain management is predictive analytics. By incorporating machine learning algorithms, businesses can analyze historical data to forecast future trends. This capability empowers organizations to anticipate changes in demand, thereby adjusting inventory strategies accordingly. Predictive analytics facilitates proactive decision-making rather than reactive responses, ultimately saving costs and improving customer satisfaction. Additionally, combining predictive analytics with edge computing ensures real-time adjustments based on newly derived insights to refine processes continuously. Companies can adapt their supply chains quickly, responding to unforeseen market changes and customer expectations. For instance, businesses can track weather patterns that may affect transportation schedules or assess seasonal demand variations. Enhanced visibility into these factors ensures optimal performance across the supply chain. Furthermore, predictive analytics applications minimize the likelihood of supply chain disruptions by identifying potential risks early on. This prevents delays and improves overall responsiveness. Identifying opportunities for improvement and optimizing resource allocation becomes vital through predictive insights. Companies harnessing these tools enhance overall supply chain performance and create lasting business value.
Encouraging collaboration among supply chain stakeholders is vital in today’s interconnected business landscape. Edge computing supports seamless communication within supply chains, providing real-time updates to all partners involved. This improved collaboration assists in aligning strategies across different entities. Enhanced information sharing allows everyone from suppliers to customers to stay informed of changes throughout the supply chain. As a result, coordination improves significantly, reducing inefficiencies and enhancing overall performance. Collaborative platforms fueled by edge computing enable partners to work together more effectively, fostering innovation. Consequently, problems are identified and solved faster, better ensuring that supply chain objectives are met. For example, manufacturers can coordinate with suppliers to adjust production schedules based on real-time data insights from devices at the edge. This synergy allows for agile responses to external market demands. Moreover, strengthening collaboration leads to improved resilience throughout the supply chain. By understanding interdependencies between partners, companies can develop contingency plans to address potential challenges collectively. Implementing edge computing facilitates this necessary collaboration, laying the groundwork for robust future supply chain adaptability and performance.
Conclusion: A Future of Efficiency
The future of supply chain management lies in embracing advancements like edge computing to foster efficiency. Companies can optimize operations and create more responsive strategies through localized data processing. Enhanced data security, reduced operational costs, real-time visibility, and improved collaboration are just a few advantages of implementing edge computing. As businesses increasingly adopt these technologies, those lagging behind risk losing their competitive edge. Embracing predictive analytics further empowers companies to anticipate customer needs, ensuring timely responses. The integration of IoT devices amplifies these benefits, providing invaluable data streams that enhance decision-making. Businesses that prioritize these innovations will not only streamline their supply chains, but they’ll also enhance customer satisfaction through more reliable service delivery. This emphasis on efficiency prompts organizations to rethink traditional practices, focusing on sustainability and agility. As market dynamics evolve, the role of edge computing becomes more pivotal. Organizations must recognize edge computing’s potential to reshape their supply chains and invest in the necessary infrastructure. In conclusion, those who harness the capabilities of edge computing are poised to drive meaningful transformation within their supply chains, preparing for future challenges and opportunities with confidence.
Globally, the demand for agile supply chains continues to rise as businesses face pressures to innovate and respond to shifts in consumer preferences.